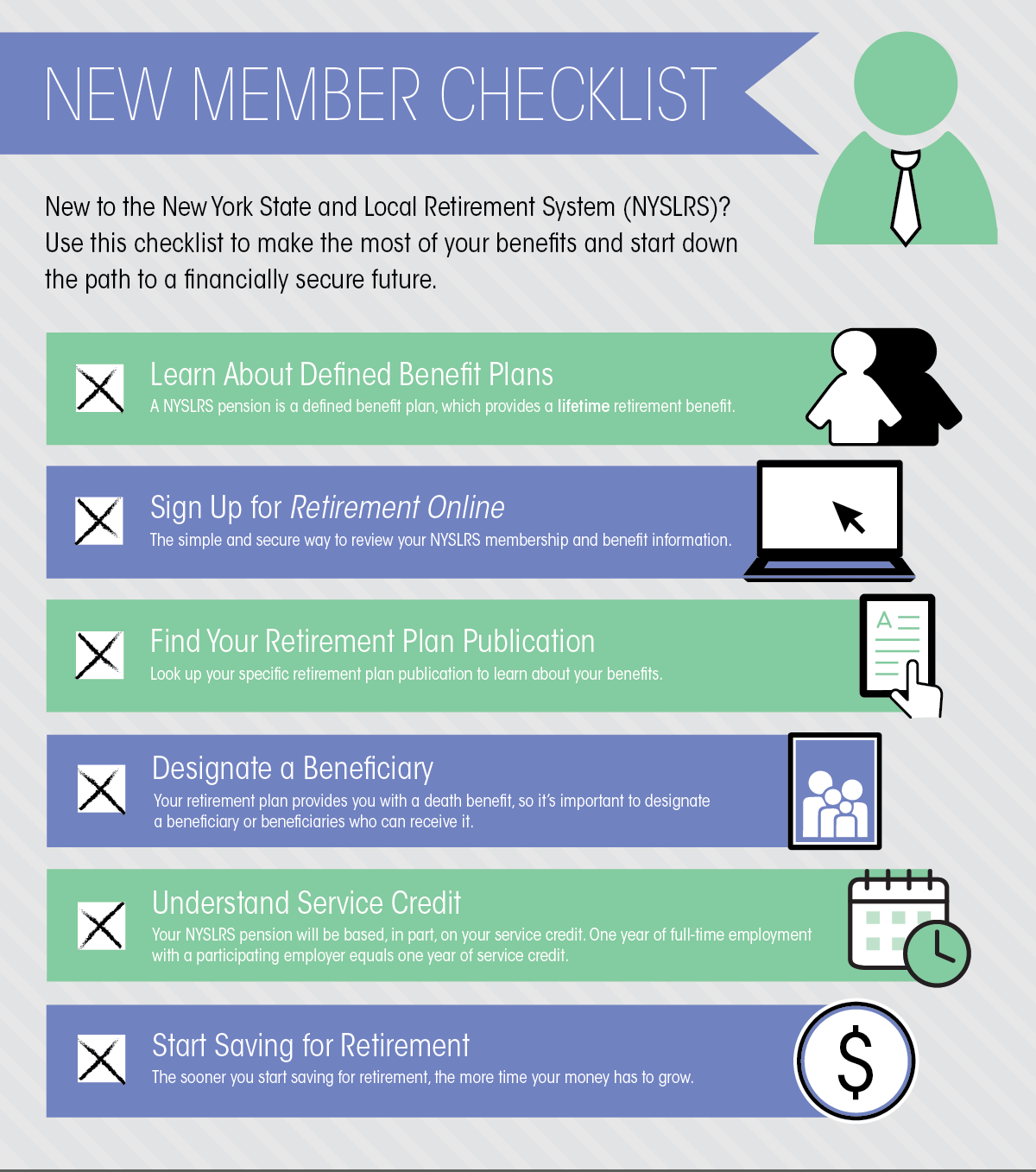
Financial security doesn’t just happen; it takes planning and time. You know you can count on your NYSLRS pension income in retirement. But, if you want to improve your chances of a financially secure retirement, your plan should include personal savings. It’s important to start saving and investing early so your money has time to grow.
You might invest in an Individual Retirement Account (IRA) or a 401(k)-style retirement savings plan. When you do, you earn a return on your investment, and those returns are compounded. That means your money increases in value by earning returns on both the original amount and your accumulated profits. This is different than earning simple interest. Let’s see how they both work.
How Simple Interest Works
In banking, simple interest is a certain percentage you are paid on the money you put in your account. With simple interest, the amount of interest you earn is based on the original (or principal) amount of the deposit.
Let’s say you open a Certificate of Deposit (CD) which pays 5 percent simple interest if you agree to keep your money in the CD for a year. If you deposit $1,000 in January, you’d have $1,050 at the end of the year. That’s $50 more than you started with, so you might decide to keep your money there for another year. With simple interest, the interest you earn the second year and every year after would still be based on the principal amount of $1,000—no compounding.
How Compounding Works
With compounding, your initial investment plus your earnings are reinvested. If you earn the same 5 percent, with compounding, it’s applied to the full balance of your account. So, you would still have that $1,050 at the end of the first year, but by the end of the second year you’d have $1,102.50 in your account instead of $1,100.
In this example, that’s just a difference of $2.50, but, over time, compounding can mean a difference of hundreds or thousands of dollars.

If you’re thinking about boosting your personal savings for retirement, look for accounts using compound interest. For example, the New York State Deferred Compensation Plan (NYSDCP) is the 457(b) plan created for New York State employees and employees of other participating public employers in New York. The sooner you can start saving, the more time your money has to grow.