Estimating your post-retirement expenses is crucial to effective retirement planning, and it’s important to remember that taxes are also part of that equation. Most retirees pay less in taxes than when they were working, partly because their incomes are lower. But there are other reasons why your tax burden may be lighter after you stop working.
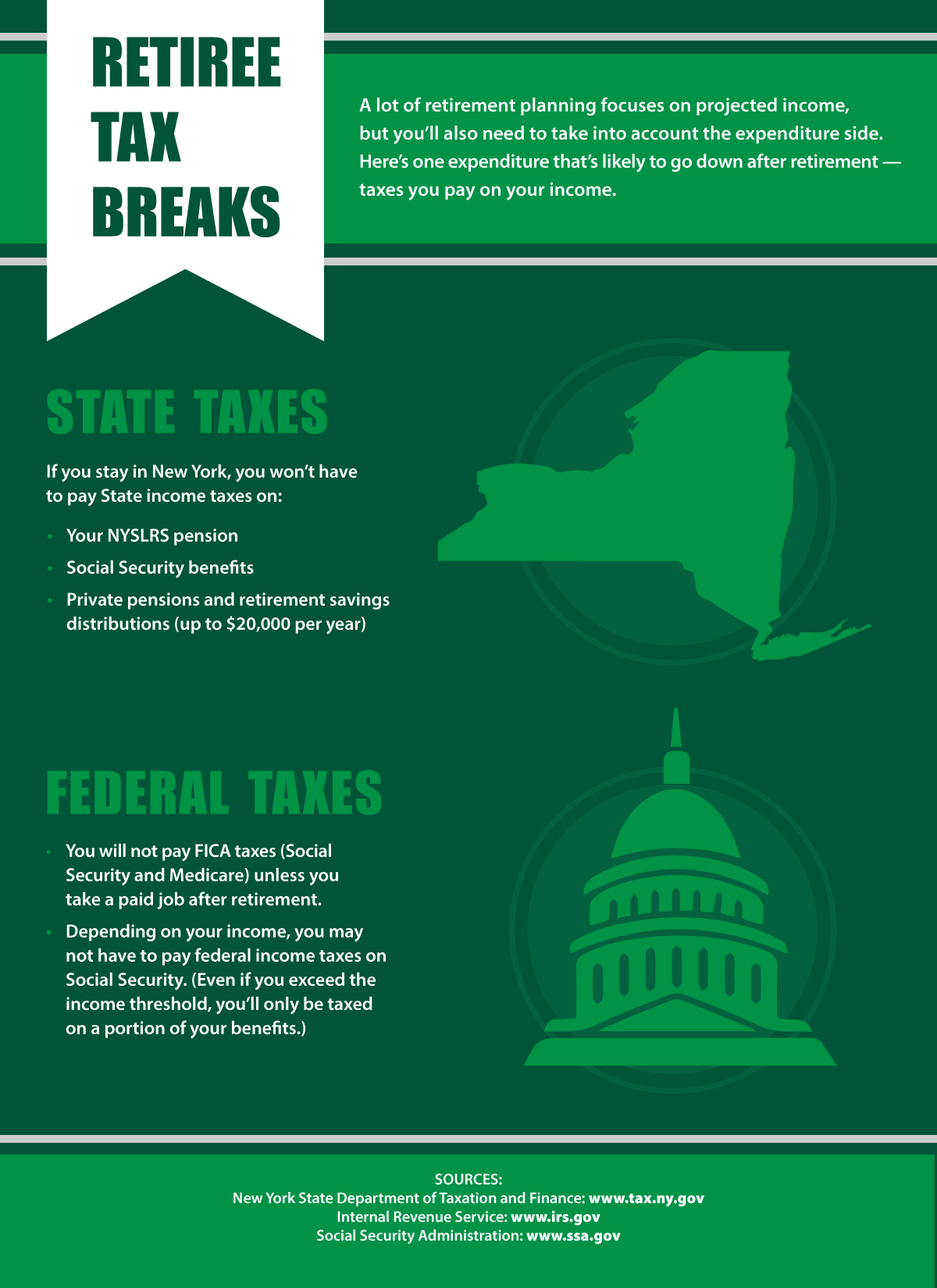
New York State Taxes
As a NYSLRS retiree, your pension will not be subject to New York State or local income tax. New York doesn’t tax Social Security benefits, either.
You may also get a tax break on any distributions from retirement savings, such as deferred compensation, and benefits from a private-sector pension. Find out more on the Department of Taxation and Finance website.
Be aware that you could lose these tax breaks if you move out of New York. Many states tax pensions, and some tax Social Security. For information on tax laws in other states, visit the website of the Retired Public Employees Association.
Federal Taxes
Unfortunately, most of your retirement income will be subject to federal taxes, but there are some bright spots here.
Your Social Security benefits are likely to be taxed, but at most, you’ll only pay taxes on a portion of your benefits. You can find information about it on the Social Security Administration website. (If you’re already retired, use the Social Security Benefits Worksheet in the Form 1040 instructions to see if any of your benefits are taxable.)
Throughout your working years, you’ve paid payroll taxes for Social Security and Medicare. For most workers, that’s 6.2 percent (Social Security) and 1.45 percent (Medicare) of your gross earnings out of every paycheck. But Social Security and Medicare taxes are only withheld from earned income, such as wages. Pensions, Social Security benefits and retirement savings distributions are exempt from Social Security taxes. Of course, if you get a paying job after retirement, Social Security and Medicare taxes will be deducted from your paycheck.
Once you turn 65, you may be able to claim a larger standard deduction on your federal tax return.
To better understand how your retirement income will be taxed, it may be helpful to speak with a tax adviser.
















 Let’s say you work as a firefighter, so you’re a member of PFRS. You decide to take on a part-time job as a bus driver for your local school district. Your school district participates in ERS, so you’re eligible for ERS membership. You fill out the membership application, and now you’re a member of both ERS and PFRS. The date you join each system determines
Let’s say you work as a firefighter, so you’re a member of PFRS. You decide to take on a part-time job as a bus driver for your local school district. Your school district participates in ERS, so you’re eligible for ERS membership. You fill out the membership application, and now you’re a member of both ERS and PFRS. The date you join each system determines 