Small towns and rural areas in New York and across the United States get an important economic boost from public pensions, a recent study concludes.
Why Public Pensions Give an Economic Boost
Because of their smaller economies, less-populated counties benefit more from pension dollars than larger, urban counties, according to Fortifying Main Street: The Economic Benefit Of Public Pension Dollars In Rural America.
In many small towns and rural communities, the report notes, school districts and local governments are the largest employers. Those public employees typically remain in their communities after retirement, and the authors attribute the economic boosts they found to pension dollars spent locally on goods and services.
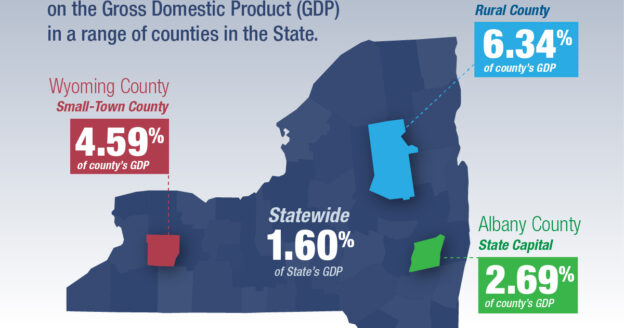
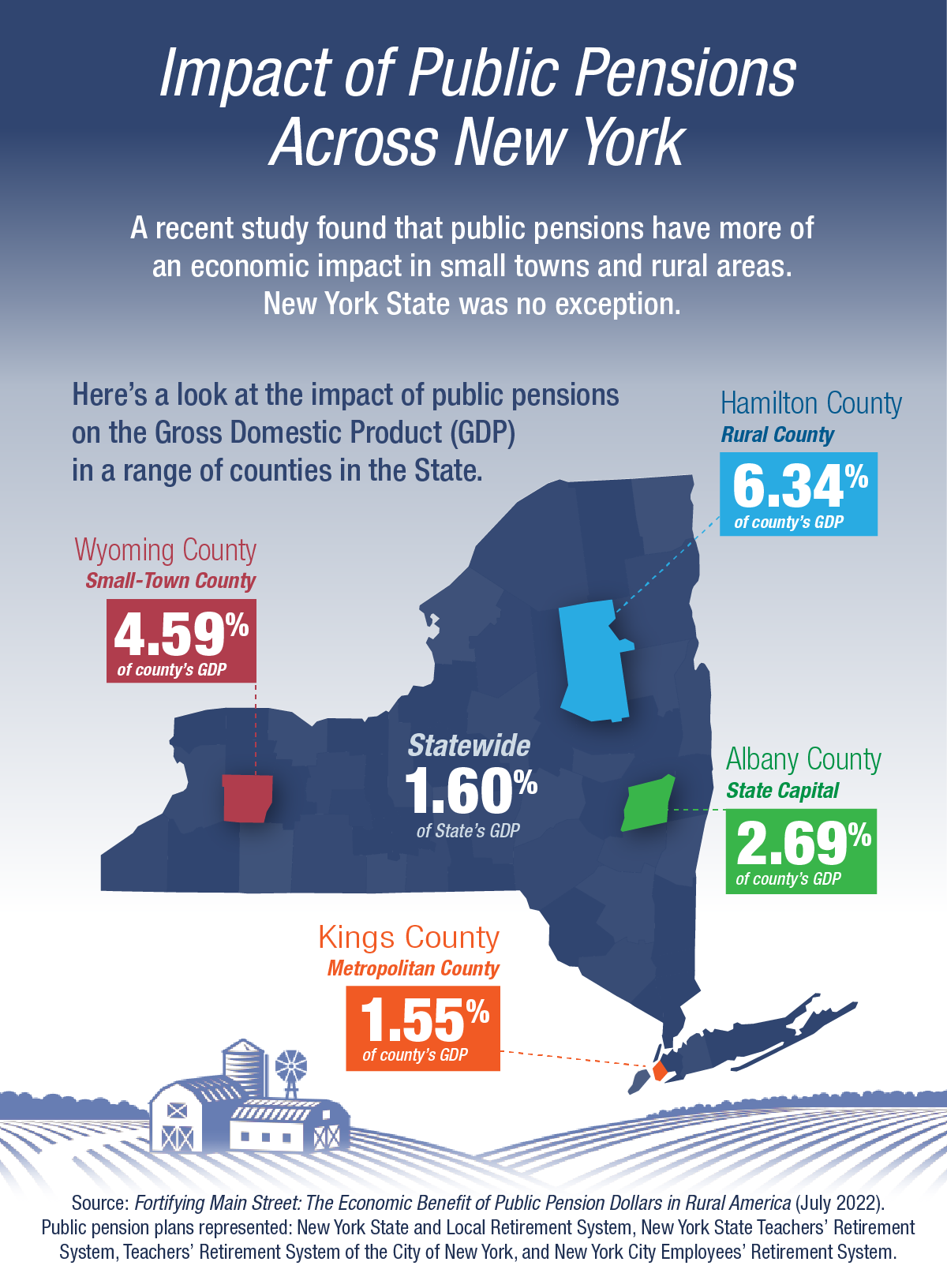
Across New York State, public pensions were responsible for 1.6 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2018. (GDP, the total value of goods and services produced during a specific period, is a common gauge of economic activity.) However, during the same period:
- Wyoming County in western New York, where a handful of villages dot a rural landscape, saw public pensions generate 4.6 percent of GDP.
- Hamilton County, with fewer than 5,000 people, received an economic boost from public pensions that accounted for 6.3 percent of GDP.
The study’s findings are in line with data showing the impact NYSLRS retirees have on local economies and other studies about the economic benefits of pensions.
Notes on the Data
Fortifying Main Street, which was released in July by the National Institute on Retirement Security (NIRS), examines pension data from 2,922 counties in 43 states. Based on criteria used by the federal Office of Budget Management, it divides counties into three main categories: metropolitan, small-town (or micropolitan) and rural. The study also analyzes data from counties that are home to the state capital, because these places tend to have higher numbers of public retirees. In Albany County, public pensions generated 2.7 percent of GDP.
Hamilton County is the only county in New York defined as rural in the study, but 16 counties, including Wyoming County, fit the “small town” criteria. You can read the full report on the NIRS website.
The study uses pensions paid by NYSLRS, the New York State Teachers’ Retirement System, the Teachers’ Retirement System of New York City and the New York City Employees’ Retirement System in its data for New York State.